Arduino UNO Project Ideas with Code and Circuit Diagram
Arduino is a very popular open-source platform and Arduino UNO is one of the most loved microcontrollers among electronics hobbyists worldwide. It consists of a physical programmable circuit board and an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that allows the writing and upload of computer code to the board very effortlessly. Due to its user-friendly environment and huge community support, it become the first choice for beginners in this field.
In this article, we will go through some of our best Arduino UNO projects that you can make at home easily and understand the functions and workings of Arduino UNO. All the Arduino project ideas listed below were built on Circuit Digest and you can get them complete code and circuit for all projects completely for free by just clicking on the respective links. That being said let's get started with this article.
1. Building your own Sun Tracking Solar Panel using an Arduino:
Traditionally, solar panels are fixed and the movement of the sun over the horizon means that the solar panel does not harness maximum energy most of the time.
![]()
This arduino UNO project introduces a Sun-tracking system project using an Arduino Uno, a servo motor, and LDRs to optimize solar panel efficiency. Hardware components, circuit connections, and assembly instructions are provided, along with step-by-step code explanations for the project. The project concludes by emphasizing the practical applications of the system and potential enhancements for larger solar panels.
Link: Building your own Sun Tracking Solar Panel using an Arduino
2. Bluetooth Controlled Pick and Place Robotic Arm Car using Arduino:
This fun arduino project outlines the construction of a Bluetooth-controlled robotic arm using an Arduino board and servo motors, emphasizing precision-controlled movements in robotics.
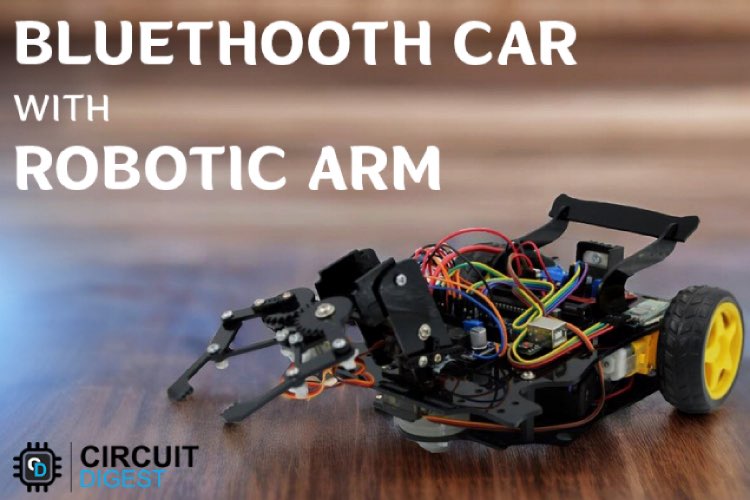
It provides insights into the arm's kinematics and the significance of understanding forward and inverse kinematics equations. The Arduino tutorial highlights the assembly process, circuit connections, and code implementation, emphasizing the role of servo motors and the Android application for wireless control. Overall, the project serves as an educational introduction to robotics and automation, showcasing the fusion of hardware and software in creating a versatile and interactive mechanical system.
Link: Bluetooth Controlled Pick and Place Robotic Arm Car using Arduino
3. Smart Dustbin using Arduino:
The Arduino Smart Dustbin Project is an innovative solution for waste management, utilizing an Arduino Nano, servo motors, an HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, and an IR sensor.

The project's objective is to automatically open the lid upon detecting nearby objects, promoting cleanliness and sanitation. The circuit design emphasizes proper voltage regulation through a buck converter, ensuring the system's stability. The code involves monitoring sensor inputs and controlling servo motors to facilitate smooth lid movement. Overall, the project aligns with the "Swatch Bharat Mission," encouraging a clean and eco-friendly environment through hands-free waste disposal.
Link: Smart Dustbin using Arduino.
4. DIY Arduino Bluetooth Car Controlled by Mobile Application:
If you are a beginner and enjoy building robots, this is likely the first Arduino project you will do after learning the basics, which is why we decided to build a Wireless Bluetooth Controlled Robot Car Using Arduino.

The Wireless Bluetooth Controlled Robot Car is a beginner-friendly Arduino project with an Android app for control and RGB Neopixel LEDs. It requires components like Arduino UNO, HC05 Module, L298N Motor driver, NeoPixel LEDs, etc. The onboard chassis building process and motor connections are detailed..The Arduino Project code utilizes SoftwareSerial.h for Bluetooth communication and controls robot movements and LED lights. The Android app, built with MIT app inventor, enables users to send commands to the robot via Bluetooth.
5. Build your own Mars Rover Robot using Arduino:
This cool looking Arduino Project presents the construction of an Arduino-based Mars rover, emphasizing design, components, and assembly. It highlights the role of the L298N motor driver and HC-05 Bluetooth module in movement and control.

Detailed circuit diagrams and code explanations aid technical understanding, with an Android app enabling rover control. The project encourages exploration in robotics, electronics, and programming, fostering curiosity and creativity in space exploration. The planet Mars has captivated our imagination for centuries, and the idea of sending rovers to explore its surface has fueled our curiosity even further.
Link: Build your own Mars Rover Robot using Arduino
6. DIY Self Balancing Robot using Arduino:
This Arduino Project is not for beginners as it outlines the construction of a self-balancing robot using an Arduino, including component selection, 3D printing, and assembly.
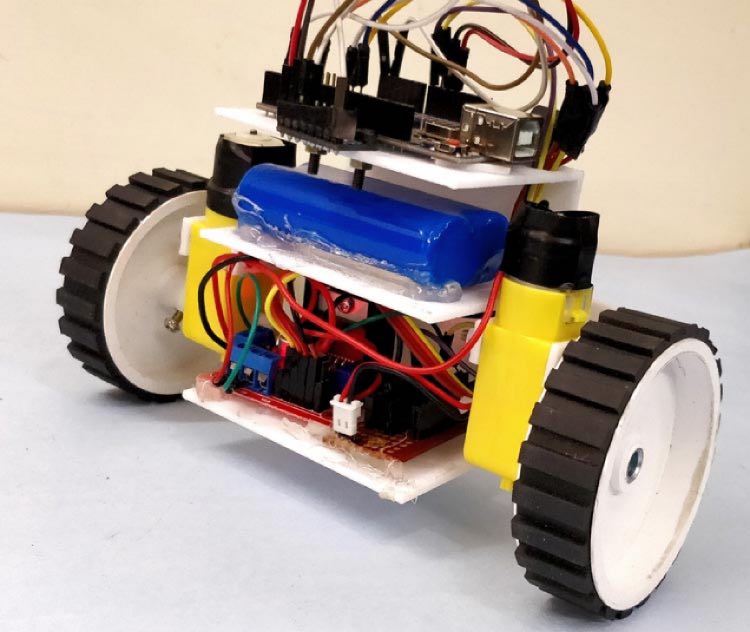
It covers the circuit diagram and the PID algorithm's implementation for achieving self-balancing, emphasizing the significance of tuning PID values. The guide provides troubleshooting tips and instructions for ensuring the project's success. This way I would be able to grasp the underlying concept behind all these scooters and also learn how the PID algorithm works.
Link: DIY Self Balancing Robot using Arduino
7. Building an easy Line Follower Robot using Arduino Uno:
The Line Following Robot (LFR) is quite an interesting Arduino project to work on! In this tutorial, we will learn how to build a black line follower robot using Arduino Uno and some easily accessible components.
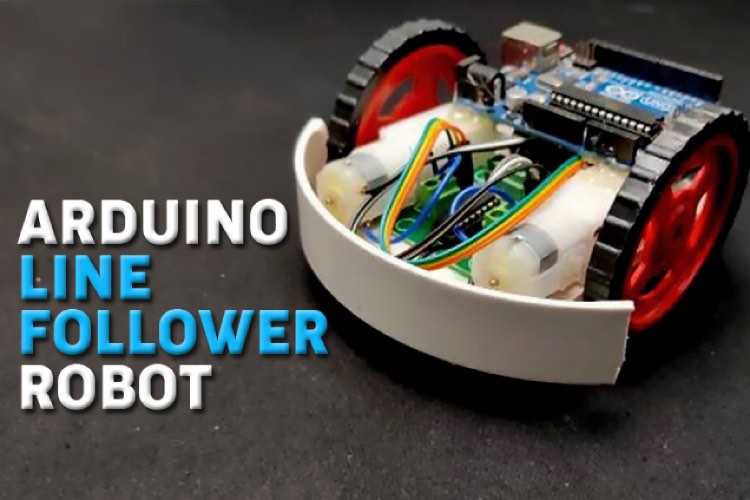
The Line Follower Robot (LFR) uses IR sensors to follow lines on the ground autonomously, navigating with four actions: forward, left turn, right turn, and stop. The project requires an Arduino Uno, an L293D motor driver, IR sensor modules, a battery, BO motors, and a hobby robot chassis. The circuit integrates sensors, motor driver, motors, and Arduino, with the motor driver ensuring proper motor control. The code uses basic Arduino functions to define the robot's actions based on sensor outputs. Calibration involves adjusting the IR module's variable resistor, ensuring accurate line detection. Detailed assembly instructions and a video demonstration are provided for the project.
Link: Building an easy Line Follower Robot using Arduino Uno
8. DIY Arduino Based Color Sorter Machine using TCS3200 Color Sensor:
The color sorting machine employs a TCS3200 color sensor, Arduino UNO, and servo motors for automated color-based sorting of objects into designated boxes.

Its applications span diverse industries like agriculture, food, and mining where color identification is essential. The project involves building a robotic arm using a Sunboard sheet, and the program logic utilizes the servo library and a detectColor() function to determine and sort colors. Detailed step-by-step instructions and a video demonstration are provided for reference. Some application areas include the Agriculture Industry (Grain Sorting on the basis of color), the Food Industry, the Diamond and Mining Industry, Recycling, etc.
Link: DIY Arduino Based Color Sorter Machine using TCS3200 Color Sensor
9. Human Following Robot Using Arduino and Ultrasonic Sensor:
This Arduino UNO Project is not only fun to build but also is really exiting to watch it work. One exciting application of robotics is the development of human-following robots.

This article presents the development of a human-following robot with Arduino and three ultrasonic sensors, highlighting its advantages over conventional designs. It outlines the necessary components and the circuit diagram, emphasizing the crucial connections required for the project. The Arduino code demonstrates how the robot functions based on the input from the sensors, enabling it to measure distances and adjust its movements accordingly. The article underscores human-following robot's versatility and potential applications, citing their relevance in various sectors such as retail, security, entertainment, and elderly care.
Link: Human Following Robot Using Arduino and Ultrasonic Sensor
10. Automatic Irrigation System using an Arduino Uno:
This Arduino UNO project details the creation of an Automatic Irrigation System using an Arduino Uno and a soil moisture sensor.
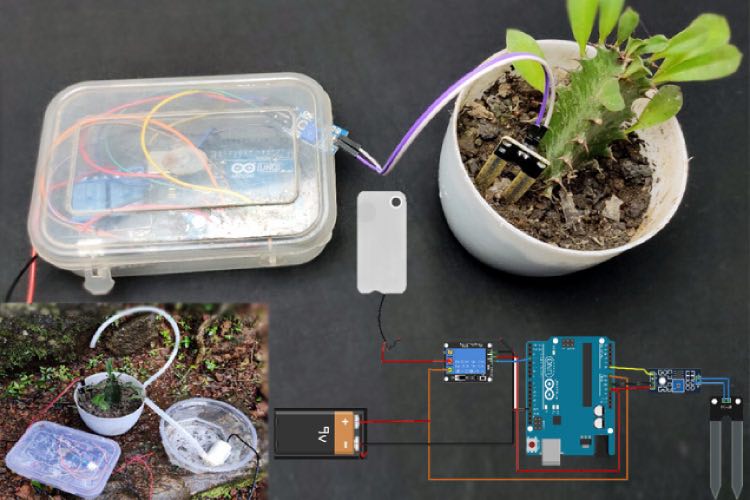
The sensor measures soil moisture, triggering the water pump when levels are low and stopping it when the soil is adequately hydrated. A relay module facilitates pump control, while a 5V battery powers the circuit. The code, without libraries, reads sensor data, converts it to a percentage, and operates the pump based on predefined moisture thresholds. The guide includes a circuit diagram, assembly steps, and calibration instructions, making it accessible for beginners.
- Read more about Arduino UNO Project Ideas with Code and Circuit Diagram
- Log in or register to post comments









 Bill Schweber is a contributing writer for Mouser Electronics and an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times and as the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.
Bill Schweber is a contributing writer for Mouser Electronics and an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times and as the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.